Table of Contents
- Understanding Procrastination
- The Science Behind Procrastination
- Procrastination Among Gen Z and Millennials
- What is Mindfulness?
- Mindfulness and the Brain
- How Mindfulness Can Help Overcome Procrastination
- Enhancing Self-Awareness
- Managing Emotions
- Cultivating a Non-Judgmental Approach
- Practical Mindfulness Techniques to Combat Procrastination
- Mindful Time-Blocking
- Visualization
- Creating a Mindful Environment
- The Role of Mindful Interventions in Long-Term Change
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR)
- Building a Supportive Community
- Measuring Progress and Celebrating Success
- Conclusion
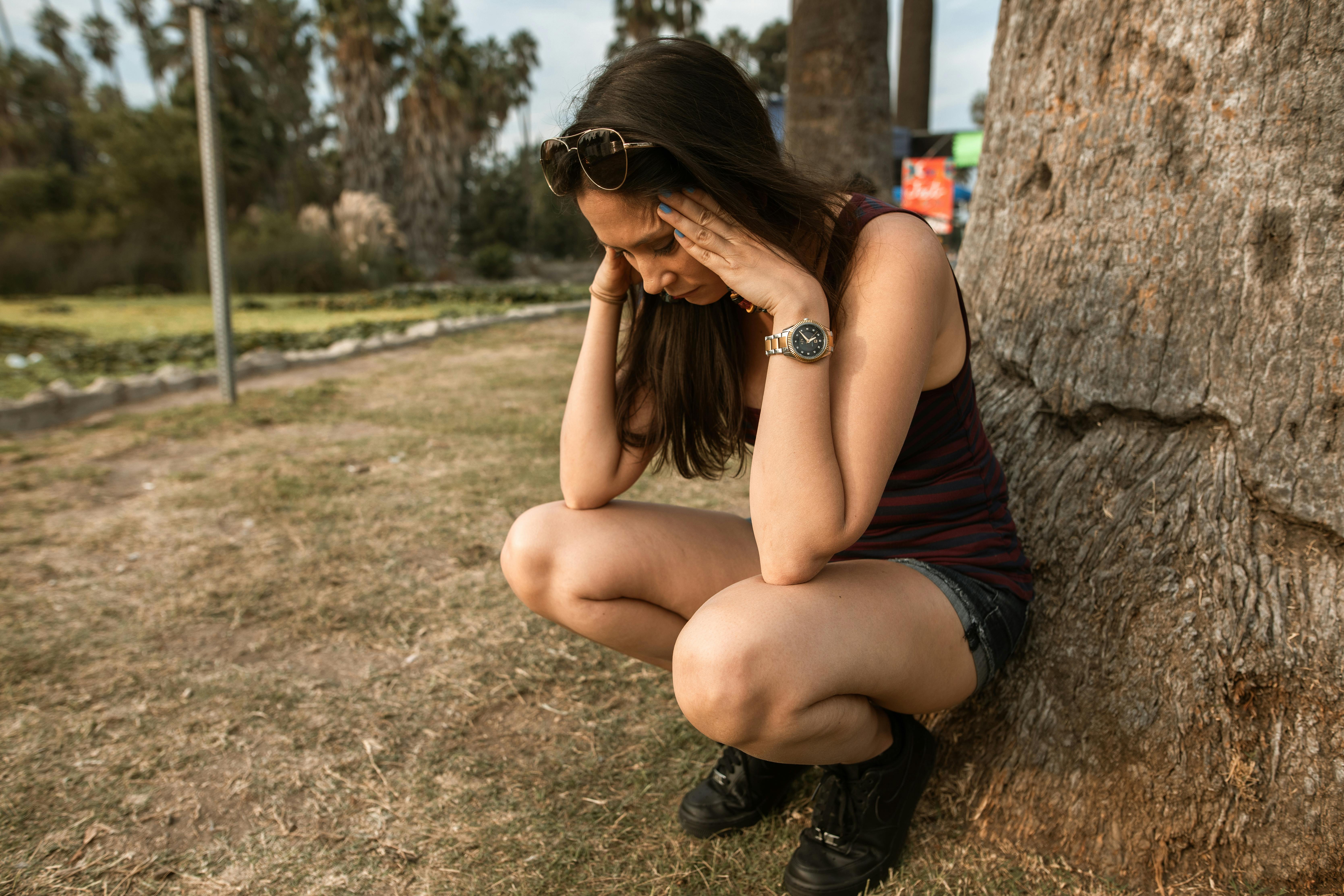
Understanding Procrastination
Procrastination—a familiar adversary for many—clamors for attention, often causing stress and denting productivity. Gen Z and Millennial women, in particular, find juggling careers, education, and personal life challenging, leading to increased procrastination. This exploration delves into how mindfulness techniques can tackle procrastination effectively, while drawing on scientific backing to provide actionable strategies.
The Science Behind Procrastination
It’s tempting to dismiss procrastination as mere laziness. But it’s much more—it’s a nuanced psychological behavior. A study published in the Psychological Bulletin in 2007 (Steel) describes procrastination as a delaying tactic, even when it means negative outcomes. The roots? Self-doubt, fear of failure, and perfectionism often play a part.
Science Behind Procrastination
Research has been revealing. The limbic system of our brain—seat of emotions and instant gratification desires—plays a significant role in procrastination, as indicated by Tuckman in 1991. When tasks appear, our prefrontal cortex, which oversees planning and decision-making, gets trumped by the limbic system. This is when we gravitate towards short-term joys, sidelining long-term benefits.
Procrastination Among Gen Z and Millennials
A YouGov survey from 2020 unveiled that 60% of Millennials and Gen Z individuals acknowledged themselves as procrastinators. They navigate digital distractions and societal pressures—a perfect storm for procrastination tendencies.
What is Mindfulness?
Mindfulness—it’s about being fully present and engaged in the moment, minus the judgment. Recognizing thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations without reacting. Studies like the one by Keng, Smoski, & Robins in 2011 demonstrate that mindfulness can enhance focus, reduce stress, and improve emotional regulation.
Mindfulness and the Brain
The brain’s response to mindfulness is remarkable. Neuroimaging studies, such as those led by Lazar et al. in 2005, show that mindfulness meditation beefs up cortical thickness in areas linked to attention and sensory processing. Plus, it shrinks the amygdala—or the fear center—mitigating anxiety that often fuels procrastination.
How Mindfulness Can Help Overcome Procrastination
Mindfulness can be powerful against procrastination—by enhancing self-awareness, managing emotions, and promoting a non-judgmental approach to our thoughts and behaviors.
Enhancing Self-Awareness
Mindfulness promotes introspection. It uncovers the roots of your procrastination. A 2014 study by Mrazek et al. found that mindfulness practitioners were better attuned to their procrastination triggers, enabling proactive management.
- Mindful Journaling: Track your daily thoughts and feelings linked to procrastination. This habit helps in spotting patterns and triggers, arming you with strategies to tackle them.
- Body Scan Meditation: This involves focusing on various body parts, fostering awareness of physical sensations. Often, it unveils stress and tension that correlates with procrastination.
Managing Emotions
Mindfulness aids in managing emotions, diminishing anxiety’s grip on actions. As detailed in the Journal of Anxiety, Stress & Coping (Sirois & Tosti, 2012), mindfulness boosts emotional regulation, reducing procrastination.
- Mindful Breathing: Spend a few minutes each day focusing on your breath. This practice soothes the mind, reducing anxiety, and disrupting the procrastination cycle.
- Loving-Kindness Meditation: This involves sending positive vibes to yourself and others, building emotional resilience, and cutting down on the negative self-talk often accompany procrastination.
Cultivating a Non-Judgmental Approach
Central in mindfulness is the non-judgmental stance toward thoughts and actions. This can diminish fear of failure and perfectionism—procrastination’s key drivers.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): This mindfulness-infused therapy champions acceptance of thoughts and feelings instead of control, which can tamp down procrastination (thanks Hayes, Strosahl, & Wilson in 1999).
- Gratitude Practice: Concentrating on what you’re grateful for can pivot your mentality from negative to positive, lessening the emotional resistance to procrastination.
Practical Mindfulness Techniques to Combat Procrastination
Incorporating mindfulness in daily routines can noticeably cut down procrastination. Here are tangible techniques:
Mindful Time-Blocking
Designate time blocks for tasks with undivided attention. It helps focus on one task at a time, easing the overwhelm that spurs procrastination.
- Pomodoro Technique: Immerse fully in a task for 25 minutes, followed by a 5-minute break. This method leverages mindfulness to boost productivity with present-focus.
- Digital Detox: Carve out regular digital breaks to curb distractions and maintain focus.
Visualization
Visualization—it’s about mentally rehearsing tasks. This can amplify motivation, softening procrastination by making tasks seem achievable.
- Goal Visualization: Picture task completion success for a few minutes each day. It can boost motivation and ensure clarity.
- Process Visualization: Dive into steps needed to complete a task—not just the end goal. It can mitigate anxiety and procrastination by breaking tasks into manageable chunks.
Creating a Mindful Environment
A cluttered space often mirrors a cluttered mind. Shaping a mindfulness-friendly environment can reduce procrastination triggers.
- Declutter Regularly: Keep your workspace tidy to avoid distractions and sustain focus.
- Mindful Motivation Board: Showcase quotes and imagery that inspire and remind you of goals.
The Role of Mindful Interventions in Long-Term Change
Mindfulness interventions can drive enduring change in procrastination habits. These practices, integrated into day-to-day life, can bolster long-term productivity and well-being.
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR)
MBSR, a program designed to leverage mindfulness for psychological wellness, is proven to reduce procrastination by enhancing focus and curbing stress (Kabat-Zinn, 1990).
- Weekly Mindfulness Sessions: Join MBSR courses to methodically weave mindfulness into your routine.
- Online Mindfulness Resources: Harness apps and online courses for convenient mindfulness practice.
Building a Supportive Community
A community can anchor mindfulness practice and fuel motivation to conquer procrastination.
- Mindfulness Meetups: Engage with local or online mindfulness circles to share experiences and learn from others.
- Accountability Partners